The overall concept behind Six Sigma was developed in 1986 by Motorola as a set of tools and techniques that could improve their overall manufacturing operation. The became a globally accepted tool and methodology that many modern-day manufacturing facilities still utilize within their operations in order to eliminate waste, cut costs, increase profitability, and more. Six Sigma is able to accurately identify and remove defect-causing elements along with reducing changeability of an operation and process.
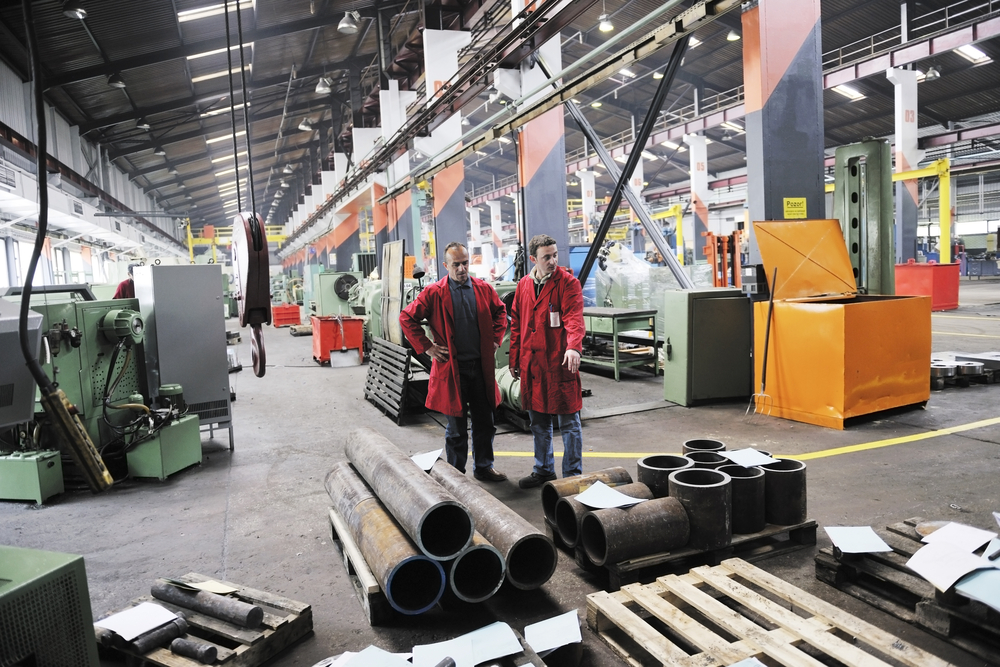

The accurately aids with the improvement of quality and outputs from a manufacturing process. Within this methodology, an organization will follow a set of steps that quantify the targeted value of a project. The application of Six Sigma in manufacturing aids the organization in pollution reduction, reduction of cycle time, and reduction of cost of production for increasing profits and customer satisfaction. In this blog, we are going to discuss how Six Sigma works and about the acronym DMAIC.
How Six Sigma Works - Features and Goals
Organizations that utilize Six Sigma set up their systems and process to include measurable metrics within manufacturing, service, and financial processes. They utilize this approach to accurately determine the projects that will best fit their overall business goals. Once a project or goal is defined, the organization follows the process known as DMAIC:
- Define: Defining the problem or need for improvement is the first step in implementation Six Sigma and applying DMAIC. This is extremely important due to the fact that without identification of a problem - you will not be able to apply the other steps. Therefore, locate the area that is in need of improvement and following through to the other steps.
- Measure: Within this step, you will measure existing systems to learn exactly what needs to be considered or a benchmark for what to compare yourself to. Measuring is a must within this process in order to determine how future performance has either increased or decreased in efficiency.
- Analyze: Analyzing pertains to the step that focuses on analyzing the system to identify ways to ultimately eliminate defects. This is able to be conducted in a variety of ways and includes a statistical analysis to determine the root cause of an issue within the process.
- Improve: During this step, project teams will seek optimal solutions and then ultimately develop and test the plan of action for improving a process or goal.
- Control: This step can be ongoing for a period of time. An organization ill implement the improvement step and then therefore modify operating instructions, policies, or procedures to help prevent future defects.
The main features pertaining to Six Sigma for improvement in the manufacturing industry pertain to having a clear understanding and focus on quantifying and measuring financial returns on a particular project. All of these features will allow an organization to easily define the responsibilities and role of every individual within the team for improving the manufacturing process of an organization.
The goal of Six Sigma production is to accurately ensure the manufacturing process to have very little defects. This pertains to having 3.4 defects per million chances is the overall ultimate goal of the system. While this may seem to be an unachievable task - most manufacturing companies achieve this final goal through adopting this technique to produce quality products.
A process that can aid with the implementation of Lean Six Sigma is Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) Software. APS Software is a cutting edge technology system that enables manufacturers to have thorough insight into their overall operation and improve their operation through bottleneck elimination and process improvement. APS can easily be integrated into manufacturing operations that are seeking to enhance efficiency within their operation and ultimately cut costs and improve profitability. APS is also compatible with various ERP, MRP, and MPS software around the globe. APS is essential for manufacturers that are seeking to maintain a competitive advantage and get ahead within their industry.
Advanced Planning and Scheduling Software
Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) software has become a must for modern-day manufacturing operations due to customer demand for increased product mix and fast delivery combined with downward cost pressures. APS can be quickly integrated with a ERP/MRP software to fill gaps where these system lack planning and scheduling flexibility and accuracy. Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) helps planners save time while providing greater agility in updating ever-changing priorities, production schedules, and inventory plans.
- Create optimized schedules balancing production efficiency and delivery performance
- Maximize output on bottleneck resources to increase revenue
- Synchronize supply with demand to reduce inventories
- Provide company-wide visibility to capacity
- Enable scenario data-driven decision making
Implementation of Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) software will take your manufacturing operations to the next level of production efficiency, taking advantage of the operational data you already have in your ERP.
Related Capacity Planning Video
APS Resources
Topics: six sigma
















LEAVE A COMMENT