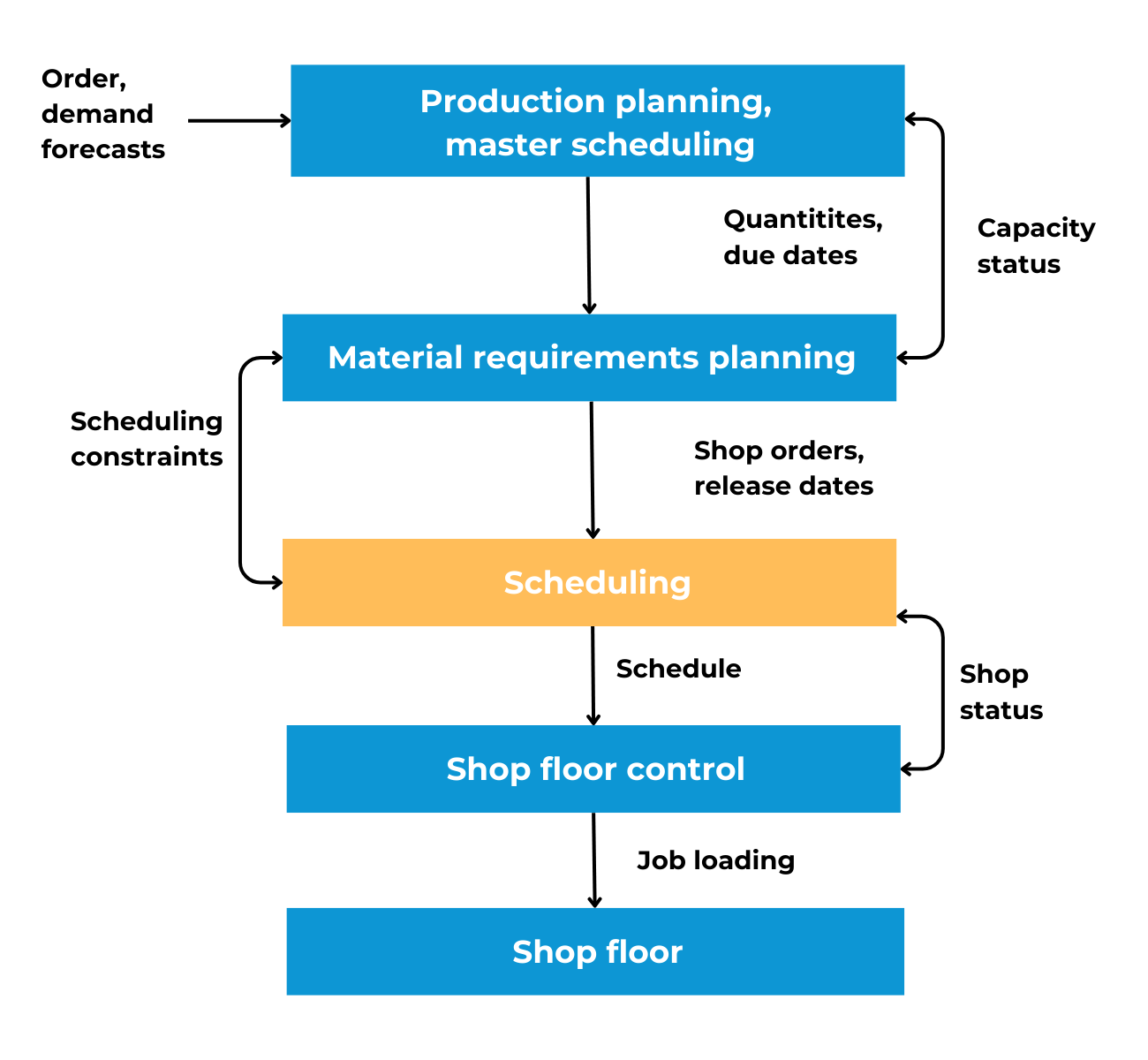
Shop Floor Control Production Software Benefits
There are various shop floor control production software benefits that can easily enhance efficiency within a manufacturing operation.
Flowcharts clarify processes, but complex flows and change make them hard to maintain. Learn pros/cons and validate improvements with what-if scheduling.
Flowcharts make work visible by mapping each step, decision point, and handoff—so teams can spot rework loops, unclear ownership, and common sources of delay. They’re most effective for repeatable workflows you want to standardize or improve. Their limits show up when processes change frequently or become highly complex, because diagrams are hard to keep current. Use flowcharts to diagnose the process, then validate changes with data and scheduling scenarios.
When working on continuous improvement projects and attempting to understand current processes on the floor, you may be looking into utilizing process flowcharts. While these charts can have some limitations, these charts can be extremely beneficial in the sense that they allow you to break down a process step by step, allocate time to the steps, and ultimately see the big picture behind a process.

A flowchart is a graphical representation of a process or algorithm. It uses different shapes and arrows to depict the steps in a sequence, decision points, and the flow of data or control from one step to another. Flowcharts are commonly used in various fields, such as programming, business process analysis, engineering, and more, to visually represent and communicate the structure and flow of a system or process.
Can be used in a variety of settings. It could be processes as complicated as creating a new motor for an engine all the way down to brushing your teeth in the morning. This is why this tool is extremely beneficial, because it allows you to visualize each step.
Process flowcharts also can aid in showcasing which steps could be combined, how new equipment or automated processes can remove steps, and ultimately a potential foundation of how you can increase efficiency within your operation. Flowcharts are being utilized by many different industries around the globe and can provide thorough insight into your operation. When utilizing flowcharts, there are a series of advantages and disadvantages associated with the tool. Therefore, within this blog we are going to discuss the advantages and disadvantages associated with process flowcharts.
Process flowcharts have a variety of advantages that can bring tremendous value to your operation. These advantages include the following:
Process flowcharts are commonly utilized by industrial engineers and individuals involved with process improvement. This tool allows you to communicate processes and potential problems on the floor in a way that management can understand, thus pushing them to potentially change up the process or implement new equipment. Communication is key when it comes to process flow charts, because it can turn a complicated procedure into a simplistic visual that allows management to understand the overall scope of the process and issues associated with it.
With the help of flowcharts, issues on the floor are able to be analyzed in a much more effective manner that showcases potential areas of cost reduction and time allocation. This is beneficial in the sense that you can take a look at steps that may be able to be combined or rearranged, leading to reduced waste and more output per hour. Process flowcharts are an advantageous method in being able to analyze the process and ultimately looking for areas of improvement.
Flowcharts are an advantageous method of document processes on the floor that everyone is able to understand and ultimately can be utilized in various departments. As everyone is able to understand these flowcharts, there is more of an incentive to clean processes up through process step elimination and efficiency enhancement. Being able to document the process, explain why the process is the way that it is, and have it on hand is a substantial advantage to your facility.
The advantages of flowcharts seem endless. Unfortunately, with every pro,there is a con: disadvantages associated with flowcharts.

A few of the disadvantages pertaining to flowcharts include the following:
Alterations can become a hassle when using flowcharts. This is due to the fact that when there are alterations to the process or whenever a process needs to be changed, you will more than likely have to redraw the entire flowchart, which results in wasted time and money. By far, this is the most substantial drawback pertaining to process flowcharts.
When a process is relatively complex, this can make a process flowchart look messy and clumsy. This will make it difficult for management to understand and could be a waste of time as you attempt to pinpoint areas of waste within a certain process or area. This is why it is important to take a look at the process and see if there are any steps that can be included together or simplified.
The last major drawback pertaining to flowcharts is that flowchart symbols cannot be typed. You will have to use Word, Excel, or some other software that allows you to create shapes and plug words into them. This makes recreating flowcharts rather difficult, considering that they require shapes.
Process flow charts are an incredibly advantageous tool to utilize within manufacturing facilities, warehouses, or any other area of supply chain. A software that can aid with adequate scheduling and process enhancement is PlanetTogether’s Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) Software. Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) Software is a must for manufacturing facilities that are seeking to take their production to the next level, reduce costs, and ultimately increase profitability within the operation.
Use this quick framework to decide what to do after you create a flowchart:
Flowcharts help you understand the process, but they don’t tell you whether a proposed change will improve delivery performance once real constraints are applied. After you map the “as‑is” and “to‑be” flow, Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) can test how that work flow performs with finite capacity, changeovers, labor availability, and material timing.
With APS, teams can:
What-If Scenario Planning in APS: Compare Production Schedules
In this video, you’ll see how Advanced Planning &Scheduling (APS) supports fast, practical what-if analysis—so planners can compare alternative schedules before making changes on the shop floor. It’s especially useful after you’ve mapped a process with flowcharts, identified problem steps, and want to test improvements without risking service levels.
The walkthrough focuses on building and comparing scenarios that reflect real manufacturing constraints: finite capacity, bottlenecks, changeovers, due dates, and material availability. Instead of debating options in spreadsheets, teams can evaluate schedule outcomes side-by-side and understand the tradeoffs.
This is designed for production planners, schedulers, operations leaders, and ERP/MRP owners who need faster decision cycles. You’ll learn how APS helps quantify the impact of changes on on-time delivery, lead time, capacity utilization, and schedule stability—so your process improvements translate into measurable execution gains.
Flowcharts help you document and improve processes, but many teams hit a wall when they try to turn “better process ideas” into an executable schedule. That’s where planning breaks down—especially when customer priorities shift, constraints change, or you need to compare multiple options quickly.
Download our infographic that contrasts spreadsheet-based planning vs. APS scheduling to see why scenario comparison is so difficult in spreadsheets—and how APS helps planners refresh data, run what-if schedules, and communicate changes faster using the same ERP-connected operational inputs.
If you’re using flowcharts to reduce waste, eliminate steps, or redesign workflows, this infographic helps you connect those improvements to day-to-day scheduling execution—so process changes don’t stall in manual planning cycles.
You’ll take away:
A flowchart makes a process visible so teams can align on steps, decisions, and handoffs. It’s useful for clarifying ownership and spotting rework loops, bottlenecks, and unclear inputs/outputs before you change the process.
They work best for repeatable workflows—like order entry, changeovers, inspections, or material handling—where variation and handoff confusion cause delays. Flowcharts help teams standardize steps before optimizing them.
They can be time‑consuming to maintain when processes change frequently, and complex branching logic can make diagrams hard to read. A flowchart can also fall out of sync with reality if it isn’t governed and versioned.
Assign an owner, version the document, and link updates to process changes (new routing, tooling, staffing, quality holds). If a change affects cycle time, handoffs, or decision rules, the flowchart should be reviewed.
Validate the “to‑be” process using data: compare cycle times, capacity, WIP, and on‑time delivery before and after changes. When scheduling is affected, use what‑if scenarios to test whether the new workflow holds under real constraints and demand variability.
Ready to validate your process changes against real constraints? Request an APS demo to see how PlanetTogether turns flowcharts into executable schedules with finite-capacity planning and what‑if scenarios.
There are various shop floor control production software benefits that can easily enhance efficiency within a manufacturing operation.
Understanding the differences between the assembly line production process and batch production process is key for locating the best method for...
Compare job, batch, flow, mass, and process production planning. Learn what each does best and how hybrid planning improves agility and delivery.
Stay ahead in the dynamic world of manufacturing with our blog, where PlanetTogether explores the latest industry trends, challenges, and innovations. From lean production techniques to smart factory transformations, our posts provide valuable insights tailored for manufacturers of all sizes.
Whether you're seeking strategic guidance or practical tips, this blog is your go-to resource for navigating the future of manufacturing.