How Operations Management Shapes Supply Chains: Planning & Scheduling
See how operations leaders use demand planning, forecasting, and finite scheduling to build resilient supply chains—using an aerospace & defense...
Explore 12 key operations management components—forecasting, scheduling, quality, inventory, and lean—and how APS aligns demand, capacity, and execution.
Operations management turns demand into reliable output by coordinating people, machines, materials, and processes. The 12 components—forecasting, location strategy, process design, facility layout, quality management, capacity planning, inventory, scheduling, supply chain/purchasing, HR, maintenance, and performance—work together to improve cost, flow, service levels, and resilience.
Use this guide to spot gaps in your current approach, then prioritize the components that most directly affect your constraints (capacity, materials, changeovers, and delivery commitments).
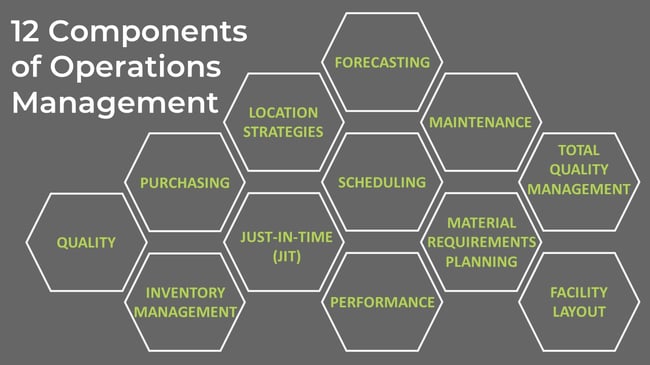
The 12 main components of operations management include the following:
The demand forecasting pertains to the process of relying on historical demand data, facts, figures, and statistics to make decisions for production. Proper demand forecasting is necessary to know how much of a specific product should be produced. This will allow your facility to only produce what is needed to avoid being stuck with excess inventory or have too many shortages.
This component of operations management involves selecting the right location for your organization. A number of factors are involved in selecting the appropriate location. For example, the location of a manufacturing facility may be decided based on the availability and proximity to certain materials or skilled labor resources. Other factors such as transportation costs can be a factor, especially if the facility is located in an area of low product demand. Together, the company’s requirements, values, and goals will help determine the best location to minimize costs and potential risks.
This component involves scheduling all of the regular maintenance checks and adjustments for your machines and equipment. Proper machine maintenance creates a safer workplace environment for your employees while reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and failures that could halt production. In addition, regular maintenance will keep your machines running at max efficiency for the longest time so that your overall production output remains high.
This component pertains to ensuring that you have enough raw materials to supply the incoming demands for products. Purchasing can be done using centralized, decentralized, or combined strategies. Centralized purchasing occurs when a single department is in charge of purchasing for the entire organization. Decentralized purchasing occurs when each department or branch is in charge of purchasing to meet their individual needs.
This component of operations management involves assigning jobs or operations to the right machine or labor resource. When an operation schedule is done right, it allows your company to decrease your overall production time and allow for more items to be produced and shipped out in time. This will allow you to increase your revenues and maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a strategy that is used to create a customer-focused organization and involves improving all employees and activities of the company to meet customer requirements. The focus of total quality management is usually on improving the processes rather than the outcomes and enables the organization to work towards having zero defects.
Materials Requirements Planning (MRP) ensures that you are receiving the right amount of the right material on time to be able to complete your production on time. MRP involves taking inventory of the items you currently have, identifying which additional materials are required, and scheduling the production of materials or their purchase.
This component is important for companies to conform to product specifications and maintain favorable relationships with their customers. Having quality products or services usually means that they meet your customer demands.
This component refers to the process of scheduling your operations so that they can start and be completed “just-in-time” - or just when they are really needed. This technique ensures that you are limiting the number of WIP items so that materials and intermediates can flow from one resource to another to avoid needing to store large quantities of WIP items.
This component is measured through examination, capacity utilization, or production. You can analyze and compare the expected time and quantity of items produced to the actual values to get a sense of whether your production facility is meeting its targets of falling short.
This component ensures that the most optimal workflow is used within your production facility. One of the 7 wastes identified in lean manufacturing involves the unnecessary movement of items throughout the facility caused by poor workflow, poor layout, and inconsistent working methods. An optimal facility layout is one that minimizes the motion of items.
This component involves keeping track of the stocked materials and items and making sure that the company is carrying the products they need at the right time. Effective inventory management will help companies meet demands by ensuring that they have the right amount of materials and finished goods to avoid having too much or too little stock.
Advanced Planning and Scheduling Software (APS) is a key software that can benefit manufacturing operations around the globe. It offers thorough insight within operations management and can take your manufacturing operation to the next level in terms of efficiency and optimization.

Modern operations management depends on getting multiple components to work together—forecasting, MRP, scheduling, inventory management, and JIT—so work flows without constant expediting. APS adds a constraint-aware planning layer that helps planners update priorities, production schedules, and inventory plans faster as conditions change.
APS also complements ERP/MRP by closing common execution gaps—especially around planning flexibility and schedule accuracy—so the plan reflects real capacity, changeovers, downtime, and material readiness.
With PlanetTogether APS, you can:
If you’re ready to reduce firefighting and move from reactive scheduling to controlled execution, see how PlanetTogether APS supports realistic, shop-floor-ready schedules.
Manufacturing teams lose time and throughput when “the plan” and shop-floor reality drift apart. This video explains how integrating Advanced Planning & Scheduling (APS) with day-to-day operations helps synchronize production priorities with real constraints—capacity, changeovers, downtime, and material readiness—so schedules are easier to execute.
If you’re in operations management, production planning, scheduling, or plant supervision, the goal is consistent execution: faster schedule updates, fewer manual handoffs, and clearer communication of what should run next. APS supports this by connecting the planning cycle to the operational workflow—so updates in demand, inventory, and production status can translate into an updated, feasible schedule without constant firefighting.
The video also highlights how PlanetTogether APS complements ERP/MRP by closing common execution gaps—improving schedule accuracy and responsiveness while supporting cross-functional coordination (supervisors, planners, purchasing, IT, and management).
Integrating planning with operations often fails for a simple reason: too much time is spent gathering updates, re-keying jobs, and manually pushing changes to the floor. When schedules depend on spreadsheets, even small disruptions can turn into hours of rework—and teams end up reacting instead of executing.
Download our infographic comparing spreadsheet scheduling vs. APS to see where planners typically lose the most time each day—and what changes when scheduling is built for manufacturing operations. It’s designed for operations leaders and planners who want more consistent execution, faster response to change, and better coordination between planning and production.
What you’ll take away from the infographic:

Commonly cited components include forecasting, location strategy, process design, facility layout, quality management, capacity planning, inventory management, scheduling, purchasing/supply chain, human resources, maintenance, and performance management. Together they turn demand into reliable, cost-effective output.
Start with the constraint that most limits throughput or on-time delivery (often a bottleneck resource, a critical supplier, or a quality gate). Improve the components that influence that constraint—capacity planning, scheduling, maintenance, and inventory buffers—before optimizing everything else.
Capacity planning determines whether you have enough labor, equipment, and time to meet demand over a horizon. Scheduling sequences specific jobs on specific resources, accounting for constraints like setups, downtime, and material readiness, to create an executable plan.
ERP/MRP systems are strong at transactions, master data, and material planning, but often rely on infinite-capacity assumptions. APS focuses on finite-capacity planning and detailed scheduling, letting teams model constraints and re-optimize quickly as priorities and conditions change.
Look for better schedule adherence, on-time delivery, throughput, lead time, inventory turns/WIP, utilization on constrained resources, scrap/rework rate, and fewer expedites. Use a small set of KPIs tied to your primary business objective.
Ready to connect forecasting, inventory, and scheduling into one executable plan? Request a PlanetTogether APS demo to see finite-capacity scheduling and scenario planning in action.
See how operations leaders use demand planning, forecasting, and finite scheduling to build resilient supply chains—using an aerospace & defense...
Stop delays and idle machines. Use a 3-step capacity planning process to match demand to resources, model scenarios, and build realistic schedules.
Resource scheduling in manufacturing is vital when it pertains to the development of a facility. Resource scheduling can efficiently schedule labor.
Stay ahead in the dynamic world of manufacturing with our blog, where PlanetTogether explores the latest industry trends, challenges, and innovations. From lean production techniques to smart factory transformations, our posts provide valuable insights tailored for manufacturers of all sizes.
Whether you're seeking strategic guidance or practical tips, this blog is your go-to resource for navigating the future of manufacturing.